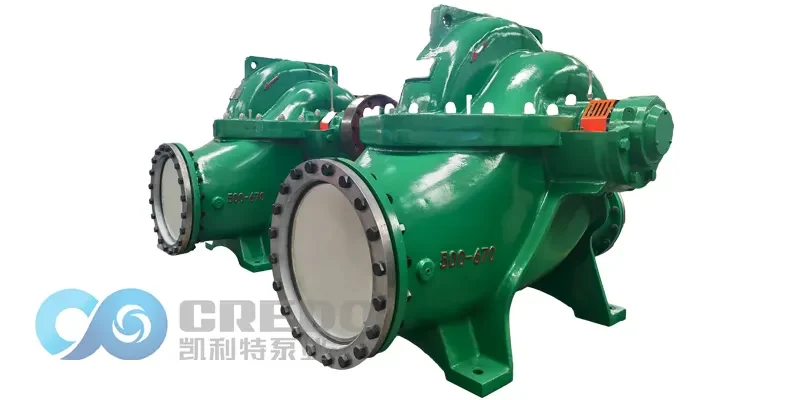
How to Design the Inlet and Outlet Pipeline of Horizontal Split Case Pump
Proper inlet and outlet pipeline design is essential for ensuring the efficient, safe, and stable operation of a horizontal split case pump. The pumps are widely used in water supply systems, HVAC, fire protection, industrial processing, and power plants due to their high flow capacity and reliability. To maximize performance and minimize mechanical issues, it is critical to adhere to best practices in pipeline layout, support, and auxiliary connections. This guide outlines key considerations for designing the suction and discharge piping for pumps.
1. Piping Requirements for Pump Suction and Discharge Piping
1-1. All pipelines connected to the pump (pipe burst test) should have independent and firm supports to reduce pipeline vibration and prevent the weight of the pipeline from pressing on the pump.
1-2. Adjustable brackets should be installed at the inlet and outlet pipelines of the pump. For pipelines with vibration, damping brackets should be installed to properly adjust the pipeline position and reduce the additional force on the pump nozzle caused by installation errors.
1-3. When the pipeline connecting the pump and the equipment is short and the two are not on the same foundation, the connecting pipeline should be flexible, or a metal hose should be added to compensate for the uneven settlement of the foundation.
1-4. The diameter of the suction and discharge piping should not be smaller than the pump inlet and outlet diameters.
1-5. The suction pipe of the pump should meet the net positive suction head (NPSH) required by the pump, and the pipe should be as short as possible with few turns. When the pipeline length exceeds the distance between the equipment and the pump, please ask the process system for calculation.
1-6. In order to prevent cavitation of the double suction pump, the elevation of the inlet nozzle pipe from the equipment to the pump should be gradually lowered, and there should be no U-shaped bend in the middle. If it is unavoidable, a bleed valve should be added at the high point, and a drain valve should be added at the low point.
1-7. The length of the straight pipe section before the pump inlet of the centrifugal pump should not be less than 3D of the inlet diameter.
1-8. For double-suction pumps, in order to avoid cavitation caused by uneven suction in both directions, the double-suction pipes should be arranged symmetrically to ensure even flow distribution on both sides.
1-9. The pipeline arrangement at the pump end and driving end of the reciprocating pump should not hinder the disassembly and maintenance of the piston and tie rod.

2. Auxiliary Pipeline Setting of the Split Case Pump
2-1. Warm pump pipeline: When the temperature of the material delivered by the centrifugal pump exceeds 200 °C, a warm pump pipeline needs to be installed so that a small amount of material is led from the discharge pipeline of the operating pump to the outlet of the standby pump, then flows through the standby pump, and returns to the pump inlet to keep the standby pump in hot standby for easy starting.
2-2. Anti-condensation pipes: DN20–25 anti-freeze pipes should be installed for pumps with condensable medium at normal temperature, and the setting method is the same as that of warm pump pipes.
2-3. Balance pipe: When the medium is prone to gasification at the pump inlet, a balance pipe that can return to the gas phase space of the upstream equipment on the suction side can be installed between the pump inlet nozzle and the pump inlet shut-off valve, so that the generated gas can flow back. To avoid pump cavitation, a cut-off valve should be installed on the balance pipe.
2-4. Minimum return pipe: In order to prevent the centrifugal pump from operating below the minimum flow rate of the pump, the minimum return pipe of the pump should be set to return a part of the fluid from the pump discharge port to the container at the horizontal split case pump suction port to ensure the flow rate of the pump.
Due to the specific design and application needs of the split case pump, it is crucial to understand the pump’s performance characteristics and the nature of the process fluid being conveyed. Properly designing the suction and discharge pipelines—including their configuration, support, and auxiliary connections—helps prevent cavitation, reduces vibration, ensures ease of maintenance, and ultimately enhances pump efficiency and reliability. By following these best practices, engineers and technicians can ensure safe, stable, and long-term operation of split case pump systems.