Understanding the Composition, Structure, and Installation Guidelines of a Vertical Turbine Pump
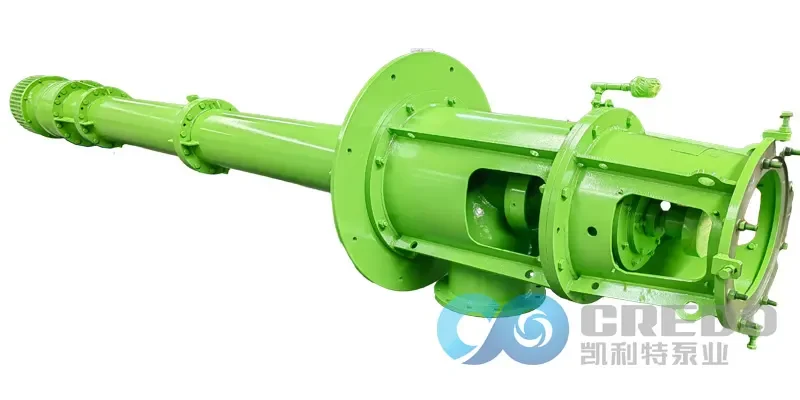
The vertical turbine pump is a highly efficient and reliable pumping solution, specifically engineered for deep well applications and high-lift water transportation. Thanks to its vertical design and multistage configuration, this pump is widely used in municipal water systems, industrial operations, and building services. Its ability to resist corrosion, handle high temperatures, and avoid clogging makes it ideal for both domestic and commercial water supply and drainage.
This article explains the main components and internal structure of a vertical turbine pump, outlines the material options for critical parts, and provides essential installation tips to ensure long-term, stable operation.
Composition and Structure of a Vertical Turbine Pump
| Components | Function |
| Driver (Motor/Engine) | Provides the power to run the pump |
| Discharge Head | Supports the motor and sends water to the discharge pipe |
| Column Pipe | Carries water up to the surface and holds the line shaft |
| Line Shaft | Transfers rotation from the motor down to the impellers |
| Bowl Assembly | Contains the stages that increase water pressure |
| Impeller | Spin the water and push it upward |
| Suction Bell / Strainer | Guides water into the pump and blocks large debris |
A vertical turbine pump consists of several key components that work together to deliver high efficiency and long service life:
These components are assembled in a modular fashion, making the vertical turbine pump easy to install and maintain. It is especially suited for deep well installations where submerged pumping is required.
Materials of Construction
The selection of materials for vertical turbine pump components depends on the specific working conditions, such as fluid temperature, abrasiveness, and corrosiveness. Common materials include:
| Components | Material |
| Discharge Head | Carbon steel/ S.S / Super Duplex |
| Column Pipe | Carbon steel/ S.S / Super Duplex |
| Line Shaft | Steel/ S.S / Super Duplex |
| Bowl Assembly | Cast Iron / Ductile Iron / Cast Steel / S.S / Super Duplex |
| Impeller | Cast Iron / Cast Steel / Ductile Iron / S.S / Super Duplex |
| Suction Bell / Strainer | Cast Iron / Ductile Iron / Cast Steel / S.S |
These materials ensure high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and long operational life, even in challenging environments.
Vertical Turbine Pump Performance Parameters
– Maximum Flow Rate: Up to 10000 m³/h
– Maximum Head: Up to 220 meters
– Power Range: Up to 5600 kW
– Operating Temperature: minus 20°C to 80°C
This wide performance range makes the vertical turbine pump a versatile solution for numerous industrial and municipal applications.

Installation Instructions for Vertical Turbine Pumps
Proper installation is crucial for achieving the expected performance and durability of a vertical turbine pump. Follow these essential guidelines:
1. Clean All Components Before Installation
During hoisting and assembly, avoid contact between parts and hard surfaces. This prevents damage and contamination by sand or debris.
2. Apply Lubrication to Threads and Joints
Use a layer of grease or butter on all threaded connections, seams, and joint surfaces to facilitate easier installation and protect against corrosion.
3. Align Shaft Couplings Accurately
When connecting the drive shaft to the coupling, ensure the ends are in full contact and the joint is centered to prevent misalignment and vibration.
4. Check Shaft-to-Pipe Concentricity
After installing each section of pipe, verify that the pump shaft is concentric with the pipe. Any misalignment should be corrected by replacing the shaft or pipe to avoid mechanical stress.
Conclusion
The vertical turbine pump stands out as a powerful and dependable option for deep well and high-head pumping tasks. Its modular design, corrosion-resistant materials, and stable performance make it ideal for municipal, industrial, and commercial applications. By understanding its internal structure and following best practices for installation, operators can ensure optimal performance, reduced maintenance costs, and extended service life.
For long-term reliability and efficiency, always follow manufacturer guidelines and perform routine inspections after installation.